Request to be a Litigation Guardian: Mental Incapacity
Fill out nowJurisdiction: Country: Canada | Province or State: Ontario
What is a Request to be a Litigation Guardian – Mental Incapacity in Ontario?
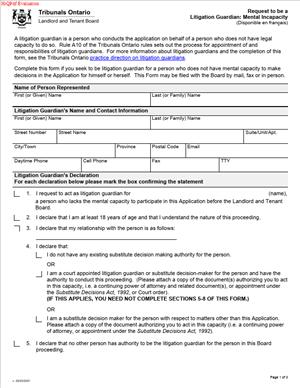
A Request to be a Litigation Guardian – Mental Incapacity in Ontario is a legal document used in the province of Ontario, Canada. It is designed for individuals who seek to become representatives for another person in legal proceedings due to that person’s mental incapacity. This form is pivotal in ensuring that individuals who cannot represent themselves in court due to mental health challenges have someone to act on their behalf, safeguarding their legal rights and interests.
Who Typically Uses This Form?
Typically, this form is used by family members, close friends, or caregivers of individuals who have been deemed mentally incapable of managing their legal affairs. Legal professionals, such as attorneys or paralegals, might also assist in the preparation and submission of this form on behalf of the applicant. The form is essential for those who are seeking to step into the role of a litigation guardian, which is a critical responsibility involving the management and decision-making in legal matters for another person.
Why Would You Need This Form?
You would need this form if you are looking to legally represent a person who cannot make decisions for themselves in a legal context due to mental incapacity. This might be necessary if the individual is involved in a lawsuit or other legal proceedings but lacks the mental capacity to understand or participate in the process. By becoming a litigation guardian, you ensure that the mentally incapacitated person’s interests are effectively represented and protected in court.
Typical Usage Scenarios
There are several scenarios where this form becomes essential. For instance, if an adult child needs to represent a parent who has developed dementia and is involved in a legal dispute, this form allows the child to legally act on behalf of the parent. Another example is when a caregiver needs to initiate or respond to legal proceedings on behalf of a mentally incapacitated patient. In such cases, the caregiver can use this form to request the court to appoint them as a litigation guardian. This ensures that the incapacitated individual’s rights and interests are not neglected during legal proceedings.
When Would You Use a Request to be a Litigation Guardian – Mental Incapacity in Ontario?
The Request to be a Litigation Guardian – Mental Incapacity in Ontario is used in various practical contexts. If you are a family member or close friend of a person who has been declared mentally incapable, and that person is involved in a legal matter, you would use this form to seek the court’s approval to represent them. Common situations include involvement in civil litigation, family law disputes, or even administrative tribunal hearings.
For example, if a mentally incapacitated individual is involved in a lawsuit concerning their property rights, and they cannot comprehend or participate in the proceedings, you would need to fill out this form to become their litigation guardian. This ensures that their interests are adequately represented and protected. Similarly, if you are caring for someone who is unable to make decisions due to a cognitive disorder, and a legal issue arises, you would use this form to request the authority to act on their behalf in legal matters.
Typical users include family members who are stepping in to manage the legal affairs of a relative suffering from mental incapacity. This could be due to conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, severe mental illness, or brain injury. Legal professionals might also use this form to assist clients in securing the right to represent their incapacitated loved ones in court proceedings.
Legal Characteristics of the Request to be a Litigation Guardian – Mental Incapacity in Ontario
This form is a legally binding document. When completed and approved by the court, it grants the applicant the authority to act as a litigation guardian for the mentally incapacitated individual. The enforceability of this form is ensured through the court’s oversight. The court reviews the application to ensure that the appointment of a litigation guardian is in the best interests of the incapacitated person and that the proposed guardian is suitable for the role.
The legal considerations around the form are significant. It must be filled out accurately and completely, as the court relies on the information provided to make a determination about the appointment of a litigation guardian. The applicant must demonstrate that the individual they wish to represent is indeed mentally incapable of managing their legal affairs. Additionally, the applicant must show that they are willing and able to act in the best interests of the incapacitated person. This involves a commitment to making decisions that protect the person’s rights and well-being.
The court’s involvement ensures that the process is fair and that the rights of the mentally incapacitated individual are safeguarded. The legal framework surrounding this form is designed to prevent potential abuse of power by the litigation guardian and to ensure that the guardianship is necessary and appropriate.
How to Fill Out a Request to be a Litigation Guardian – Mental Incapacity in Ontario
Filling out the Request to be a Litigation Guardian – Mental Incapacity in Ontario involves several steps. It is important to approach this process with care, as the accuracy and completeness of the form are crucial for its acceptance.
Step 1: Gather Necessary Information
Before you begin filling out the form, gather all relevant information. This includes the personal details of the mentally incapacitated individual, such as their full name, date of birth, and current address. You will also need your own personal information, as the applicant, including your contact details and relationship to the incapacitated individual.
Step 2: Complete the Applicant Information Section
Start by filling out the section of the form that pertains to the applicant. This includes your name, address, phone number, and your relationship to the person for whom you are seeking to become a litigation guardian. Clearly state your connection to the individual and why you are seeking this role.
Step 3: Detail the Incapacitated Individual’s Information
In this section, provide detailed information about the person you wish to represent. Include their medical condition or diagnosis that has led to their mental incapacity. It is important to provide medical documentation or a statement from a qualified medical professional that supports the claim of mental incapacity.
Step 4: Explain the Need for a Litigation Guardian
Here, you must clearly articulate why a litigation guardian is necessary. Describe any legal proceedings that the incapacitated person is involved in and explain why they cannot represent themselves. This section should highlight how your involvement as a litigation guardian would benefit the incapacitated person.
Step 5: Sign and Date the Form
After completing all sections of the form, ensure that you sign and date it. Your signature is a legal declaration that the information provided is true and accurate to the best of your knowledge.
Step 6: Submit Supporting Documents
Along with the form, submit any supporting documents that substantiate the claim of mental incapacity and your suitability as a litigation guardian. This might include medical records, letters from healthcare providers, or any other relevant documentation.
Step 7: File the Form with the Court
Once the form is complete and all supporting documents are gathered, file the form with the appropriate court in Ontario. The court will review your application, and if deemed appropriate, you will be appointed as the litigation guardian for the mentally incapacitated individual.
By following these steps carefully, you can ensure that the form is filled out correctly, increasing the likelihood of a successful application. Remember, the goal is to ensure that the incapacitated individual’s legal rights are protected and that they have competent representation in any legal matters they are involved in.
Legal Terms You Might Encounter
When dealing with the Request to be a Litigation Guardian for someone with mental incapacity in Ontario, you may come across several legal terms that are important to understand. A “Litigation Guardian” is a person appointed by the court to make legal decisions for someone who cannot make them due to mental incapacity. The term “Mental Incapacity” refers to a state where an individual is unable to understand information necessary to make a decision or cannot appreciate the consequences of making a decision.
“Applicant” is the term used for the person who is applying to become the Litigation Guardian. This person needs to demonstrate their capability to act in the best interest of the individual with mental incapacity. “Respondent,” on the other hand, is the person for whom the Litigation Guardian is being requested. This person is typically the one with the mental incapacity.
You might also hear “Guardianship Order,” which is an official document from the court granting the applicant the authority to act as a Litigation Guardian. The term “Affidavit” refers to a written statement confirmed by oath or affirmation, used as evidence in court. In this context, it might be a statement confirming the applicant’s suitability.
“Consent” in this context refers to the approval or agreement from relevant parties involved, indicating that they agree to the applicant acting as a Litigation Guardian. “Capacity Assessment” is a professional evaluation that determines someone’s mental ability to make decisions, which might be required to support the application. Lastly, “Court” denotes the legal body that has the authority to approve or deny the request for a Litigation Guardian, ensuring all procedures are followed correctly.
FAQs
Do you need a lawyer to become a Litigation Guardian?
It’s not mandatory to have a lawyer to apply for the role of a Litigation Guardian. However, considering the complexities involved, legal advice can ensure that you understand your responsibilities and that all paperwork is accurately completed.
Can you be a Litigation Guardian for multiple people?
Yes, you can apply to be a Litigation Guardian for more than one person, provided you can demonstrate the ability to manage the responsibilities for each individual effectively. Each application must be made separately.
How long does it take to get approved as a Litigation Guardian?
The duration varies depending on the court’s schedule and the completeness of your application. Generally, it can take several weeks to a few months. Ensuring all documents are correctly filled out and submitted can help expedite the process.
What happens if the court denies your application?
If your application is denied, you will receive a notice explaining the reasons. You may have the option to amend your application or appeal the decision. Consulting a legal professional can provide guidance on how to proceed.
Do you need to renew your status as a Litigation Guardian?
Once appointed, a Litigation Guardian usually retains their status unless the court orders otherwise or if there are changes in the person’s mental capacity. However, you may need to provide periodic updates or reports to the court.
Are there costs involved in applying to be a Litigation Guardian?
Yes, there might be filing fees and other costs associated with the application process, including potential costs for obtaining a capacity assessment. It’s wise to budget for these expenses when preparing your application.
Can you resign as a Litigation Guardian?
Yes, if you can no longer fulfil your duties, you must apply to the court to be released from your responsibilities. The court will then decide on the next steps, possibly appointing another guardian.
What if the person regains mental capacity?
If the person you are acting for regains mental capacity, you should inform the court. A reassessment might be conducted, and the guardianship could be terminated if the court deems the person capable of making their own decisions again.
Checklist: Before, During, and After
Before Signing:
Ensure you have all necessary documents, including identification, capacity assessments, and any relevant medical records. Gather affidavits from professionals or other parties supporting your application. Verify that you understand the responsibilities involved in being a Litigation Guardian.
During Signing:
Review each section of the form carefully. Check that all personal information is accurate and complete. Ensure any required signatures are obtained and that you have completed any sections regarding consent and understanding of your responsibilities.
After Signing:
File the form with the appropriate court office. Keep a copy of the completed form for your records. Notify any relevant parties, such as family members or healthcare providers, of your application. Store all documents securely, as you might need them for future reference or updates to the court.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Don’t forget to provide complete and accurate information. Missing details can delay the process or result in denial. Ensure all supporting documents, such as capacity assessments and affidavits, are included. Omitting these can weaken your application.
Avoid submitting without understanding your responsibilities. Being a Litigation Guardian involves significant duties. Failing to understand these can affect your ability to act effectively and may lead to legal consequences.
Don’t neglect to communicate with involved parties. Keeping family or other stakeholders informed is crucial. Lack of communication can lead to disputes or misunderstandings about your role.
What to Do After Filling Out the Form
After completing the form, your first step should be to submit it to the appropriate court office. Ensure you follow the court’s specific filing procedures, which may include paying a filing fee. Once filed, keep a copy of the submission confirmation for your records.
If your application is approved, follow any instructions provided by the court regarding your new responsibilities. If amendments are necessary, address them promptly to avoid delays. Stay in touch with any legal advisors or relevant parties throughout this process to ensure you meet all obligations.
Disclaimer: This guide is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as legal advice. You should consult a legal professional.